

The effect of the blade velocity on the compression factor is shown using a Parametric Sweep. The model uses the new Rotating Frame feature, which applies centrifugal and Coriolis forces to the particles, allowing the trajectories to be computed in a noninertial frame of reference that moves with the rotating blades. In this example, the trajectories of gas molecules are computed in the empty space between two rotating blades of a turbomolecular pump. For turbomolecular pumps, in which the blades move at speeds comparable to the thermal speed of the gas molecules, a Monte Carlo approach is needed.
Laminar flow module comsol 5.3 free#
The Free Molecular Flow interface available in the Molecular Flow Module is an efficient tool for modeling extremely rarefied gases when the gas molecules move much faster than any geometric entities in the domain. A Donnan potential shift over the interface is calculated automatically from the concentrations of the charge-carrying ion on each side of the interface.Number density (1/m 3) inside a vacuum chamber fed with a small capillary tube, modeled using half the geometry with a Plane Symmetry.Īpplication Library path for an example that uses the Plane Symmetry boundary condition: Molecular_Flow_Module/Industrial_Applications/differential_pumping New Tutorial: Turbomolecular Pump OMSOL Multiphysics version 5.5 includes the new Metal Processing Module and Porous Media Flow Module extended and improved versions of the Application Builder, COMSOL Compiler, COMSOL Server, and COMSOL Multiphysics as well as updates and improvements for all COMSOL Multiphysics add-on products. This condition is typically used in electrochemical cells containing both free electrolytes and ion-exchange membranes, for instance, in dialysis problems. Most of our business is generated from our clients. Our Ivyland manufacturing facility has over 45,000 square feet of state-of-the-art manufacturing and engineering equipment.
Laminar flow module comsol 5.3 portable#
The new Ion-Exchange Membrane boundary node specifies a boundary condition where the flux of ions is continuous, but where the electrolyte potential is discontinuous and is described by a Donnan equilibrium. Our lines include: Laminar Flow Systems, Isolators, Ceiling Modules, Ceiling Grids, Portable Cleanrooms, Pass Thrus, Cleanroom Furniture and other related products. Ion-Exchange Membrane Internal Boundary Condition in the Tertiary Current Distribution, Nernst-Planck Interface
A fraction of the impressed current goes from the sacrificial anodes (rods) through seawater, into the ship hull, out of the ship hull, through seawater and then into the oil rig structure. The oil rig structure close to the ship is cathodically polarized. Inlet 1 1 On the Physics toolbar, click Boundaries and choose Inlet. Define the inlet and outlet conditions as described below.

The no-slip condition is the default boundary condition for the fluid. For turbomolecular pumps, in which the blades move at speeds comparable to the thermal speed of. LAMINAR FLOW (SPF) On the Physics toolbar, click Heat Transfer (ht) and choose Laminar Flow (spf). Here, the stem works as an anode while the stern works as a cathode. The Free Molecular Flow interface available in the Molecular Flow Module is an efficient tool for modeling extremely rarefied gases when the gas molecules move much faster than any geometric entities in the domain. The figure here shows a ship where parts are of the hull are bare steel, where the hull may work as a bipolar electrode. The ship hull is subjected to the electric field from the cathodic corrosion system. You typically use this interface in order to reduce the meshing and solver time for large geometries, where a significant part of the geometry can be approximated as tubes along edges.Ī ship is anchored close to an oil platform. The interface uses a boundary element method (BEM) formulation to solve for the charge transfer equation in an electrolyte of constant conductivity, where the electrodes are specified on boundaries or as tubes with a given radius around the edges. The Current Distribution, Boundary Elements interface can be used for solving primary and secondary current distribution problems on geometries based on edge (beam or wire) and surface elements. This interface remains unique in its coupling with the electrochemistry interfaces for the modeling of porous electrodes.
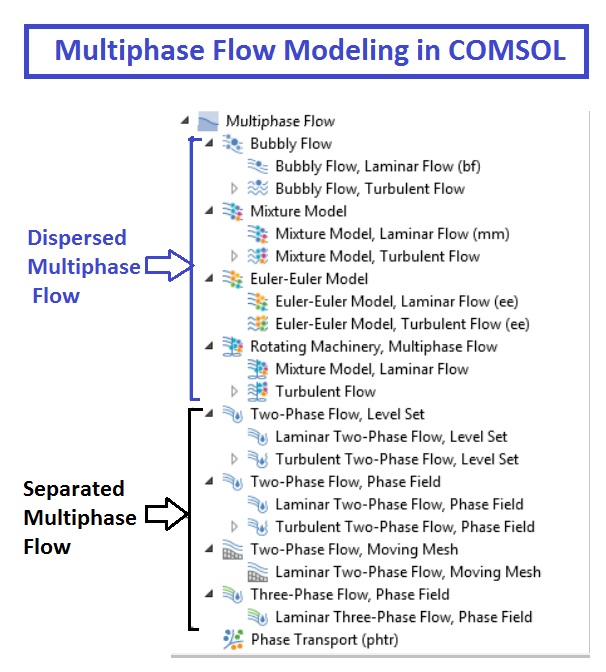
With the new version of the Free and Porous Media Flow interface, you can couple laminar or turbulent free flow with porous media flow. Current Distribution, Boundary Elements Interface Revamped Free and Porous Media Flow Interface. See all of the Electrodeposition Module updates in more detail below. For users of the Electrodeposition Module, COMSOL Multiphysics ® version 5.3 brings a new Current Distribution, Boundary Elements interface, a new Electrophoretic Flow interface, and new features in the Tertiary Current Distribution, Nernst-Planck interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
